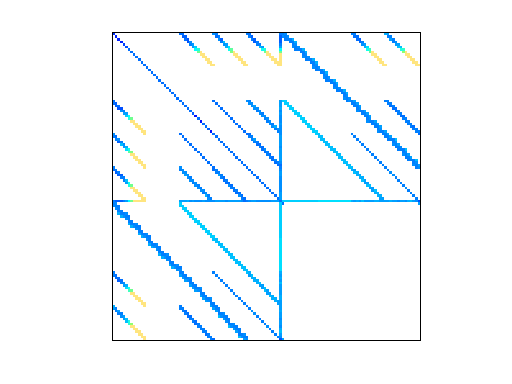
VDOL/hangGlider_1
hangGlider optimal control problem (matrix 1 of 5)
| Name |
hangGlider_1 |
| Group |
VDOL |
| Matrix ID |
2691 |
|
Num Rows
|
360 |
|
Num Cols
|
360 |
|
Nonzeros
|
3,477 |
|
Pattern Entries
|
3,477 |
|
Kind
|
Optimal Control Problem |
|
Symmetric
|
Yes |
|
Date
|
2015 |
|
Author
|
B. Senses, A. Rao |
|
Editor
|
T. Davis |
| Structural Rank |
360 |
| Structural Rank Full |
true |
|
Num Dmperm Blocks
|
1 |
|
Strongly Connect Components
|
1 |
|
Num Explicit Zeros
|
0 |
|
Pattern Symmetry
|
100% |
|
Numeric Symmetry
|
100% |
|
Cholesky Candidate
|
no |
|
Positive Definite
|
no |
|
Type
|
real |
| Download |
MATLAB
Rutherford Boeing
Matrix Market
|
| Notes |
Optimal control problem, Vehicle Dynamics & Optimization Lab, UF
Anil Rao and Begum Senses, University of Florida
http://vdol.mae.ufl.edu
This matrix arises from an optimal control problem described below.
Each optimal control problem gives rise to a sequence of matrices of
different sizes when they are being solved inside GPOPS, an optimal
control solver created by Anil Rao, Begum Senses, and others at in VDOL
lab at the University of Florida. This is one of the matrices in one
of these problems. The matrix is symmetric indefinite.
Rao, Senses, and Davis have created a graph coarsening strategy
that matches pairs of nodes. The mapping is given for this matrix,
where map(i)=k means that node i in the original graph is mapped to
node k in the smaller graph. map(i)=map(j)=k means that both nodes
i and j are mapped to the same node k, and thus nodes i and j have
been merged.
This matrix consists of a set of nodes (rows/columns) and the
names of these rows/cols are given
Anil Rao, Begum Sense, and Tim Davis, 2015.
VDOL/hangGlider
Range maximization of a hang glider optimal control problem is taken
from Ref.~\cite{bulirsch1993combining}. The goal of the optimal
control problem is to determine the state and the control that
maximize the range of the hang glider in the presence of a thermal
updraft. The state of the system is defined by horizontal distance,
altitude, horizontal velocity, and the vertical velocity and the
control is the lift coefficient. The specified accuracy tolerance of
$10^{-8}$ were satisfied after five mesh iterations. As the mesh
refinement proceeds, the size of the KKT matrices increases from 360
to 16011. This problem is sensitive to accuracy of the mesh and it
requires excessive number of collocation points to be able to satisfy
the accuracy tolerance. Thus, the size of the KKT matrices changes
drastically.
@book{bulirsch1993combining,
title={Combining Direct and Indirect Methods in Optimal Control:
Range Maximization of a Hang Glider},
author={Bulirsch, Roland and Nerz, Edda and Pesch, Hans Josef and
von Stryk, Oskar},
year={1993},
publisher={Springer}
}
|